 连接所有点的最小费用Java
连接所有点的最小费用Java
文章发布较早,内容可能过时,阅读注意甄别。
# 题目
给你一个points 数组,表示 2D 平面上的一些点,其中 points[i] = [xi, yi] 。
连接点 [xi, yi] 和点 [xj, yj] 的费用为它们之间的 曼哈顿距离 :|xi - xj| + |yi - yj| ,其中 |val| 表示 val 的绝对值。
请你返回将所有点连接的最小总费用。只有任意两点之间 有且仅有 一条简单路径时,才认为所有点都已连接。
示例 1:
输入:points = [[0,0],[2,2],[3,10],[5,2],[7,0]]
输出:20
解释:
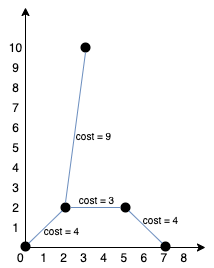 我们可以按照上图所示连接所有点得到最小总费用,总费用为 20 。
注意到任意两个点之间只有唯一一条路径互相到达。
示例 2:
我们可以按照上图所示连接所有点得到最小总费用,总费用为 20 。
注意到任意两个点之间只有唯一一条路径互相到达。
示例 2:
输入:points = [[3,12],[-2,5],[-4,1]]
输出:18
示例 3:
输入:points = [[0,0],[1,1],[1,0],[-1,1]]
输出:4
示例 4:
输入:points = [[-1000000,-1000000],[1000000,1000000]]
输出:4000000
示例 5:
输入:points = [[0,0]]
输出:0
提示:
- 1 <= points.length <= 1000
- -106 <= xi, yi <= 106
- 所有点 (xi, yi) 两两不同。
# 思路
union
# 解法
class Solution {
public int minCostConnectPoints(int[][] points) {
//MST问题 Kruskal求解
int n = points.length;
int rows = points.length;
int cols = points.length;
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(n);
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(
(a,b) -> a[2] - b[2]
);//优先级队列,保存边集,按权值从小到达排序
//保存所有边权值
for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
int[] a = points[i];
for(int j = i + 1; j < cols; j++) {
int[] b = points[j];
int value = Math.abs(a[0] - b[0]) + Math.abs(a[1] - b[1]);
pq.offer(new int[]{i, j, value});
}
}
int res = 0;
while (uf.getCount() > 1) {
int[] edge = pq.poll();//每次取出最小权值的边,加入到点集中
int a = edge[0];
int b = edge[1];
int value = edge[2];
if(uf.union(a, b)) {//能加入,计算总权值,不能加入,选择下一条边
res += value;
}
}
return res;
}
class UnionFind {
int[] parent;
int[] rank;
int count;
public UnionFind (int n) {
parent = new int[n];
rank = new int[n];
count = n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
rank[i] = 0;
}
}
public int find (int i) {
if(i != parent[i]) {
parent[i] = find(parent[i]);
}
return parent[i];
}
public boolean union (int i, int j) {
int rootI = find(i);
int rootJ = find(j);
if(rootI != rootJ) {
if(rank[rootI] < rank[rootJ]) {
parent[rootI] = rootJ;
} else if(rank[rootI] > rank[rootJ]) {
parent[rootJ] = rootI;
} else {
parent[rootI] = rootJ;
rank[rootJ]++;
}
count--;
return true;
}
return false;
}
public int getCount () {
return count;
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
# 总结
- 分析出几种情况,然后分别对各个情况实现


